Prevention of recurrent fractures in children and teenagres with low bones mineral density
V.I. Strukov, D.G. Elistratov, Yu.G. Shcherbakova, А.Т. Kuptsova, R.Т. Galeieva, L.G. Radchenko, Burmistrova L.А.
State Educational Institution DPO Penza Institute of Doctors’ Improvement; Penza
Federal state budgetary scientific institution research institute of beekeeping, Rybnoe city
Significance
The whole world is worried by multiple skeletal fractures increasing frequency, so by 2050 the growth of hip fractures will increase by 4 times. There is a significant increase in the frequency of recurrent fractures, which are also worse grow together, especially in children. Therefore, urgent attempts to reduce the predicted “epidemic of fractures” should begin as early as today and from childhood [7]. In the current domestic and foreign literature on this issue we met few publications, which indicate a lack of effective treatments and prevention of fractures [8, 9].
At present, all over the world they are trying to solve the problem of osteoporosis and bone fractures by indicating various osteo-protectors to increase the bone mineral density. We have found that this is the wrong way to go. To improve the bone mineral density and reduce the incidence of bone fractures in such a way, especially with calcium preparations is impossible because in children and adolescents there are extremely diverse pathogenetic disturbances of bone and mineral metabolism. As a result of imbalance of calcium regulatory system, the imbalance of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, the calcium that we have appointed to the patient is more stored not in bone, but in other organs and tissues with the risk of soft tissue calcification, vessels with the risk of hypermineralization, and in the future (in adults) increase the risk of strokes, heart attacks. Thus, indication of most modern osteo-protectors cannot solve the problem of osteoporosis and bone fractures, especially in the long term [5,6].
Our work is aimed at solving the above problems. We have proposed a new method for determining the therapeutic efficacy of an osteo-protector, a new method for treatment of osteoporosis, including the closure of abdominal structures (patent N 2466732). For the treatment of fractures and reduce the time of consolidation, new drugs are created, one of them will be discussed in this article.
Project aim
To explore etio-pathogenic structure of bone fractures in children and adolescents and on this basis to develop a personalized approach to treatment and prevention of bone fractures. To investigate the effectiveness of the treatment of bone diseases in children, with a new drug “Osteo-vit D3.
Material and methods of investigation
From 2007 to May 2013 on the basis of Penza Regional Children’s Hospital examined 37 children and adolescents with low bone mineral density (boys – 25, girls -12), with long bone fractures of the distal extremities, forming the main contingent. There dominated fractures of the upper extremities (28 cases), lower – (9). The study included only children and adolescents with bone fractures between the ages of 10 to 18 years. With bone mineral density (BMD) less than – 2.0 CO, with bone fractures, presence of abdominal structures in trabecular bone sections. Diagnosis was made by Z-scale below -2 CO, taking into account the BMC, BMD, presence of the main criterion – the fracture (s), height-weight parameters using tables by L.A. Sheplyagina (2013). Determination of calcium in blood serum, inorganic phosphorus, 25 (OH) D, parathyroid hormone, TSH, T3, T4.
We excluded children with secondary osteoporosis in various systemic diseases, osteogenesis imperfecta, tubulopathy, hyperparathyroidism, glucocorticoid treatment.
Evaluation of patients included medical history, physical examination, clinical, laboratory and biochemical studies: calcium, inorganic phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase, 25 (OH) D in blood serum, radiological methods. Diagnosis of vitamin D deficiency was performed by content of 25 (OH) D in the blood of less than 20 ng / ml. Determination of bone mineral density (BMD) was conducted by the X-ray absorbtion method before and after treatment in 9 -10 months on the apparatus “Osteometer” DTX-100. During the in-depth survey of the main contingent of children, three groups of causes of recurrent fractures were identified: 11 children with a deficiency of vitamin D (1 group), 7 children with the presence of bone cavities in the trabecular departments (group 2), and the rest – 19 children with low bone mineral density (group 3).
A new approach to solving the problem was the use of drone brood (drone milk) as a fortifier (amplifier) of an osteo-protector (vitamin D). The drone milk contains a high protein content (41%), amino acids (37%), including essential (about 38% of the total amount of amino acids), nucleic acids (1.1 -1.3%), enzymes (lipases, protease, phosphatase, urease, dehydrogenase, amylase, and others), phospholipids (1.1-1.5%), carbohydrates (fructose, glucose, etc.), complex lipid fractions substances, micro- and macro-cells, vitamins A, D, E, group B, and other biologically active components, so the male bee brood is called “the Bank of biologically active substances.” This composition of drone brood (milk) has curative and preventive action: antioxidant, immunomodulatory, antineoplastic, osteo-protective [1-4]. The beekeepers themselves do not have severe osteoporosis. On this basis, we have developed a “Osteo-vit D3” containing 1 tablet of 300 IU of vitamin D3 and 100mg drone brood as a corrector of metabolic processes.
Efficiency of “Osteo-vit D3” in the treatment of bone diseases is determined by the dynamics of clinical disease, bone mineral density and the closure cavity formation in bones. Children of 1 and 2 groups were receiving “Osteo-vit D3” in three-month courses three times a year 1 tab 2 times a day with monthly intervals. Children of the group 3, depending on the treatment method were divided into two subgroups of comparable age and severity of disease: subgroup A – 10 patients received “Osteo-Vit D3” 1 tablet orally 2 times daily (morning and night, i.e. 200 brood mg / day of vitamin 600IU D3 / day) in three-month courses 3 times a year. Subgroup B (control) – 9 patients received “Calcium D3 Nycomed” containing adequate amounts of vitamin D and calcium carbonate 1.0 g per a day. All the children before and after treatment in 9 -10 months had osteometry.
Investigation results
Children of the group 1 (with a deficiency of vitamin D) in treatment of Osteo-Vit had a positive dynamics of the basic clinical, instrumental and biochemical parameters. The frequency of pain and its severity in 1-2 months decreased 3-fold. There was a quick, for 7-10 days, formation of callus, compared with children not treated with “Osteo-vit D3”. Level of 25 (OH) D in 6 months of treatment increased from the “failure level” to the normal one.
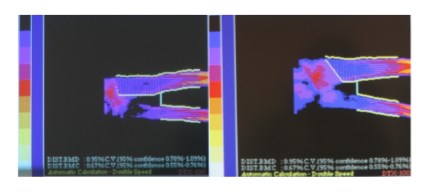
In group 2 of the patients, treated with “Osteo-vit D3” there was noted the positive dynamics in the form of extinction and reduction of pain, accelerated formation of callus, increase bone mineral density, closing of cavities or reduce their size in 2 / 3 of the patients. See. (Fig. 1)
- Patient Vanya P., 15 years. Cavity before treatment. After the treatment the cavity closed.
Fig. 2. Patient А. Cavities before treatment. After the treatment they closed.
One-third of patients in the group 2 received a positive result. These children have expressed disturbances in the hormonal status (sex hormone deficiency, dysfunction of the thyroid and parathyroid glands).
Comparative analysis of effectiveness of the therapy with “Osteo-vit D3” and “Calcium D3 Nycomed” in the group 3 showed that “Osteo-vit D3” was superior to “Calcium D3 Nykomed” to increase BMD and closing of cavity formation.
Discussion of results and conclusions
The structure of reduced bone mineral density and causes of bone fractures in children, aimed at examination was non-uniform and pediatric deterministic. It was found that especially in children with recurrent fractures there should be evaluation for deficiency of Vitamin D – the main cause of reduced bone mineral density in children. These data are consistent with the available literature data on widespread vitamin D deficiency (Holick MF 2007).
In presence of cavity formation in trabecular bones in children with fractures must be tested for hormonal status and eliminate osteopathy endocrine genesis (thyroid dysfunction is well compensated by the use of a thireo-vit (bloodroot white), insufficiency of sex hormones compensated by andro-vit (homogenate of drone brood). This will enhance the effectiveness of the treatment and it is important for prevention of recurrent fractures. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer, chronic gastroduodenitis, malabsorption) can cause reduced bone mineral density and bone fractures. At these diseases there reduced absorption of calcium in these sections of the intestine (R.T. Galeeva, 2009). Thus in view of the data there can be more reason to consider bone fractures in children with low salinity due to a variety of pediatric diseases, and without taking into account these factors one can not prevent recurrent fractures, especially in catamnesis.
“Osteo – vit D3” was used in the treatment of all investigated groups of patients with a positive result. Preparation improves the absorption of calcium from dairy products and thereby increases bone mineral density. In catamnesis in children who received three treatment courses with osteo – vit is not checked, no case of recurrent fractures. This can be explained by the fact that it reduces the frequency of falls by improving bone mineralization, strengthen ligaments and muscular system. Further research is needed in catamnesis.
Conclusions:
- Etio-pathogenetic structure of low bone mineral density in children with fractures of long bones is non-uniform and pediatric – determined by various factors: D deficiency states, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, insufficient consumption of dairy products without vitamin D, dysfunction in the endocrine system and other factors.
- Introduction of “Osteo-vit D3” for prevention and treatment of bone tissue in children and adolescents, will greatly reduce the incidence of bone fractures, vitamin deficiency rate
- In the study of the comparative effectiveness of Osteo-vit D3 with “Calcium D3 Nykomed,” Osteo-vit D3 surpassed it on the closure and reduction of cavity formation, bone fracture consolidation rate by 7-9 days.
Literature:
- Beliaiev V.A., Safonovskaia E.V. Adaptogenic properties of the drug on the basis of drone brood / / magazine “Beekeeping”. – 2009. – No.6. – p.52-53.
- Budnikova N.V. Biologically active compounds in the drone brood // Magazine “Beekeeping”. – 2009. – No.6. – p.52
- Dubcova E.A. Clinical and experimental study of the use of bee products in the treatment of some diseases of the digestive system. Abstract of the project of medical sciences candidate CRI gastritis, Moscow, 2007.
- Strukov V.I., Galeieva R.T. et al. Current osteoporosis problems. “Rostra”, 2009. p.341.
- Strukov V.I., Yelistratov D.G. etc. -. Known and new technologies in the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis. Penza – 2012.
- Shilin D.E. Modern strategy to overcome the deficiency of calcium and vitamin D in children and adolescents from the standpoint of prevention of osteopenia and fractures. // Questions of Practical Pediatrics. – 2006. – V. 1. – No. 2. – p. 50-56.
- Holick MF 2007 VitamiD deficiency/ N Engl J Med 357:266-281
- Cooper С., Dennison Е.М., Leufkens H.G.M., Bishop N., van Staa T.P. Epidemiology of Childhood Fractures in Britain: A Study Using the General Practice Research Database. // J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004.-Vol. 19.-No. 12.-P. 1976-1981.